I am going to install a reverse proxy setup with Jenkins via nginx. In my scenario I am running Jenkins in docker and mapped port 8080 to host 8080 port.
We have to install nginx, letsencrypt packages on server.
apt update
apt install nginx python3-certbot-nginx -y
I am using Ubuntu so below are commands to install letsencrypt in Ubuntu.
apt install letsencrypt [/terminal]
First create temp vhost.conf file to generate ssl. Put below content in this file /etc/nginx/conf.d/Jenkins.conf
NOTE: Please change your domain name with my domain name.
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name jenkins.devopstechy.online;
access_log /var/log/nginx/reverse-access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/reverse-error.log;
location / {
root /var/www/html/;
}
}
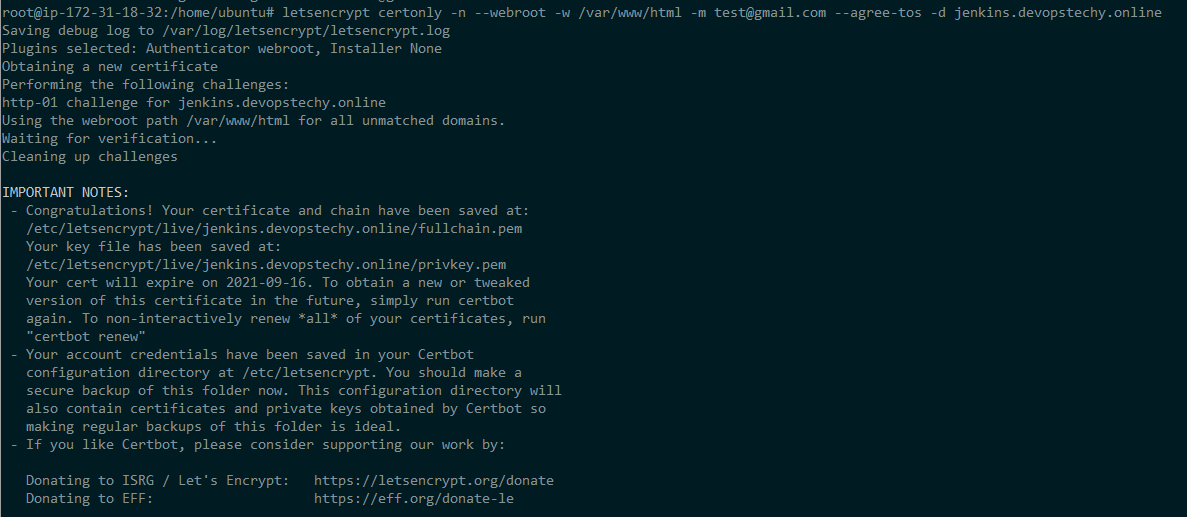
Now run below command to generate letsencrypt
NOTE: Make sure you have opened 80 and 443 port in your firewall.
letsencrypt certonly –nginx -n –webroot-path /var/www/html -m test@gmail.com –agree-tos -d jenkins.devopstechy.onlineand output like below
Now put below content in that file.
/etc/nginx/conf.d/Jenkins.conf
server {
listen 443 http2 ssl;
server_name jenkins.devopstechy.online;
access_log /var/log/nginx/jenkins.devopstechy.online-access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/jenkins.devopstechy.online-error.log;
location /.well-known/acme-challenge/ {
root /var/www/html; # Temp for generating letsencrypt
default_type text/plain;
}
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $host:$server_port;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# Fix the “It appears that your reverse proxy set up is broken” error.
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080;
proxy_read_timeout 90;
proxy_redirect http://127.0.0.1:8080 https://jenkins.devopstechy.online;
# Required for new HTTP-based CLI
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_request_buffering off;
}
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/jenkins.devopstechy.online/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/jenkins.devopstechy.online/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # managed by Certbot
ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # managed by Certbot
}
server {
if ($host = jenkins.devopstechy.online) {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
} # managed by Certbot
listen 80;
server_name jenkins.devopstechy.online;
return 404; # managed by Certbot
}
For auto renew set up cron job with below command monthly
letsencrypt –renew-by-default certonly –nginx -n –webroot-path /var/www/html -m test@gmail.com –agree-tos -d jenkins.devopstechy.online && service nginx reloadNow we have generated SSL successfully. Lets configure nginx with ssl.
Now create file /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf with below content.
# This file contains important security parameters. If you modify this file
# manually, Certbot will be unable to automatically provide future security
# updates. Instead, Certbot will print and log an error message with a path to
# the up-to-date file that you will need to refer to when manually updating
# this file.
ssl_session_cache shared:le_nginx_SSL:10m;
ssl_session_timeout 1440m;
ssl_session_tickets off;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers off;
ssl_ciphers “ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384”;
Now run below command te generate dhparams.pem. It took little bit time to complete and output like below.
openssl dhparam -out /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem 2048
Now test you nginx configuration and there should be no error in configuration and output should be like below.
nginx -t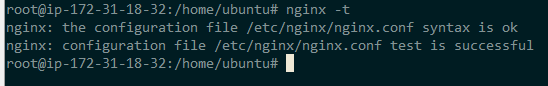
Now reload nginx configuration
service nginx reloadWe have successfully setted up letsencypt. Now go to browser and hit url and it should redirected to https like below:
Also, read Configure Nginx as a Reverse Proxy on AWS EC2 Instance 2023






